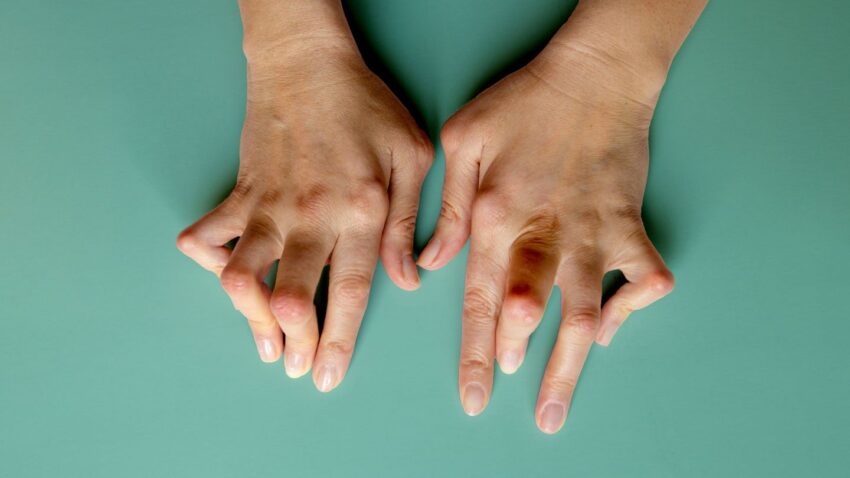
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the joints, RA can significantly impact the quality of life for those diagnosed with the condition. While there is no known cure for rheumatoid arthritis, numerous strategies and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and potentially achieve long-term relief. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various approaches to alleviate the symptoms of RA and discuss potential avenues for achieving permanent relief.

Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Before delving into potential cures, it is essential to have a basic understanding of rheumatoid arthritis. Unlike osteoarthritis, which primarily affects the joints due to wear and tear, RA is an autoimmune disorder. The immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and eventually joint damage.
Which Doctor Is Best For Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Determining the most suitable doctor for rheumatoid arthritis involves consulting with your primary care physician initially. They may advise further evaluation by a rheumatologist or an orthopedist, specializing in the management of inflammatory conditions such as arthritis.
Holistic Lifestyle Changes:
- Healthy Diet: Adopting a nutrient-rich, anti-inflammatory diet is a crucial step in managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory properties, such as fatty fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact exercises can help maintain joint flexibility and reduce stiffness. Activities like swimming, walking, and yoga can be beneficial. Consult with a healthcare professional or a physical therapist to design a personalized exercise routine that suits your specific needs.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate RA symptoms. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can positively impact both physical and mental well-being.
Medical Interventions:
- Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): DMARDs, such as methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine, are commonly prescribed to slow down the progression of RA by suppressing the immune system. These drugs, when used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, can help manage symptoms effectively.
- Biologic Response Modifiers: Biologics, including drugs like adalimumab and etanercept, target specific components of the immune system involved in the inflammatory process. These medications are often used when traditional DMARDs prove insufficient.
- Steroids: Corticosteroids may be prescribed for short-term relief of severe symptoms. However, their long-term use carries risks, and they are usually not considered a permanent solution.
Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture: Some individuals with RA report relief from pain and stiffness through acupuncture. While more research is needed to establish its efficacy, acupuncture is considered a safe complementary therapy when administered by a qualified practitioner.
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs, such as turmeric and ginger, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating herbal supplements into your routine, as they may interact with medications.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold to affected joints can provide temporary relief. Hot packs, warm baths, and cold compresses can help reduce inflammation and soothe discomfort.
The Role of Diet and Supplements:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements, have anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit individuals with RA. Consult with a healthcare professional before adding supplements to your diet.
- Vitamin D: Adequate levels of vitamin D are essential for bone health. Some studies suggest a potential link between vitamin D deficiency and RA severity. Sun exposure and vitamin D supplements may be beneficial, but individual needs vary.
Conclusion:
While there is currently no definitive cure for rheumatoid arthritis, a multi-faceted approach combining conventional medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies can significantly improve symptoms and enhance overall well-being. It is crucial for individuals with RA to work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their unique needs. By adopting a holistic perspective and remaining open to a combination of strategies, individuals can strive for effective symptom management and a higher quality of life despite the challenges posed by rheumatoid arthritis.
Read More:-Top 10 Yoga Tips Asanas For Better Eyesight
Read More:- The Top 7 Health Insurance Plans for Families