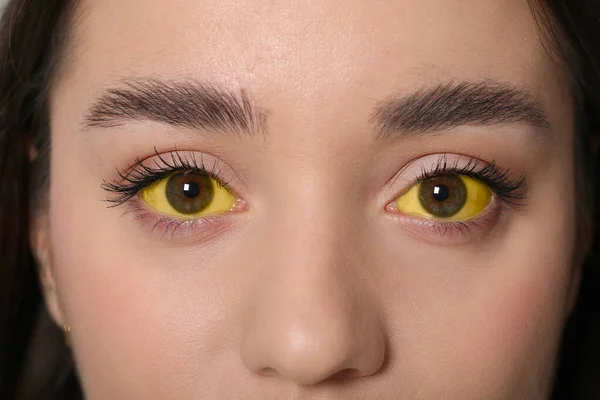
In the realm of medical conditions, few have a visual impact as striking as jaundice. The vivid yellow hue that characterizes individuals suffering from jaundice can capture attention and curiosity alike. But what is jaundice disease, and what lies beneath this striking appearance? In this article, we will embark on a journey to explore the intricacies of jaundice, from its causes to its effects on the human body and available treatments.
The Basics of Jaundice
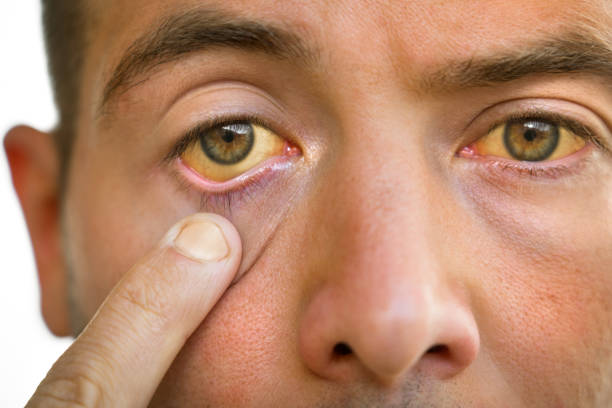
Jaundice, also referred to as icterus, isn’t a standalone condition; instead, it manifests as a symptom of an underlying medical condition. It becomes evident through the observable yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes (sclera). This distinct yellow coloration results from an elevated level of bilirubin in the bloodstream.
Bilirubin, a golden hue resulting from the breakdown of red blood cells, typically undergoes hepatic metabolism and is expelled through bile, ultimately exiting the body through feces; however, in cases of jaundice, an impediment disrupts this natural course, leading to the buildup of bilirubin within the system.

Causes of Jaundice
Jaundice can arise from a multitude of factors, generally falling into three primary categories
Pre-hepatic Jaundice manifests when an abundance of red blood cells undergoes accelerated breakdown. A frequent contributor to this condition is hemolytic anemia, wherein the body’s rate of red blood cell destruction outpaces its production capacity.
Symptoms and Effects
Aside from the most noticeable symptom, yellowing of the skin and eyes, jaundice can present other symptoms, which may include:
Dark urine: Bilirubin can cause urine to appear darker than usual.
Pale stools: The absence of bilirubin in the intestines can lead to pale or clay-colored stools.
Fatigue: Jaundice can be accompanied by general fatigue and weakness.
Abdominal discomfort can be a distressing symptom for individuals with jaundice, and its severity can vary depending on the underlying cause.
Treatment Options
The approach to jaundice treatment is intricately tailored to the specific underlying cause, with a paramount focus on rectifying the root problem while effectively alleviating the accompanying symptoms.
Managing the underlying condition: Treating the condition responsible for jaundice is crucial. This may involve medication for liver diseases, surgery to remove bile duct obstructions, or addressing hemolytic anemia through blood transfusions.
Phototherapy: A common treatment for neonatal jaundice, it harnesses a special light to facilitate the breakdown of bilirubin in a newborn’s skin.
Embracing lifestyle shifts: Opting for changes in one’s daily habits, like adjusting dietary choices and steering clear of alcohol or specific medications, can be advised to effectively handle jaundice.
Conclusion
Jaundice serves as a vivid warning signal, signaling the presence of diverse underlying health conditions. Though the noticeable yellowing of one’s skin and eyes might capture immediate attention, it’s crucial to grasp that jaundice is not an ailment in itself; rather, it serves as a telltale sign of an underlying issue. Comprehending its root causes and potential consequences is the initial stride towards accurate diagnosis and treatment, affording individuals the opportunity to reclaim their well-being and the radiant allure of their innate skin complexion.
Read More:- Calendula Flower: A Flowing Plant Aiding In Restoring Skin Health!
Read More:-Exploring the Multifaceted World of Tea: Unearthing Its Unexpected Effects


